Software Engineering
🔳What is Software ?
🔴Software is defined as a collection of computer programs, procedures,
rules and data.
🟢Software is a program or set of programs containing instructions that
provide the desired functionality.
🟠Software is a set of instruction used to acquire inputs and to manipulate
them to produce the desired output in terms of functions and performance as
determined by the user of the software.
🟡Software = Programs + Documentation + Operating procedures
🔳What is Software Engineering ?
🔸Software Engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing,
and maintaining software.
🔸It is systematic and disciplined approach to software development that
aims to create high-quality, reliable, and maintainable software.
🔸Software engineering is the establishment and use of sound engineering
principles in order to obtain economically software that is reliable and
works efficiently on real machines.
🔳Explain characteristics of software
1. Software is developed or engineered; it is not manufactured in the
classical sense.
🔸Although some similarities exist between software development and
hardware
manufacture, the two activities are fundamentally different.
🔸In both activities, high quality is achieved through good design, but
the
manufacturing phase for hardware can introduce quality problems that are
non
existent (or easily corrected) for software.
🔸Both activities are dependent on people, but the relationship between
people
applied and work accomplished is entirely different.
🔸Software costs are concentrated in engineering. This means that
software
projects cannot be managed as if they were manufacturing
projects.
2. Software doesn't "wear out."
However, the implication is clear software doesn't wear out.
But it does deteriorate!
🔸This contradiction can best be explained by considering the
“actual curve” shown in Figure.
🔸During its life, software will undergo change (maintenance). As
changes are made, it is likely that some new defects will be introduced,
causing the failure rate curve to spike as shown in figure.
🔸Before the curve can return to the original steady-state failure
rate, another change is requested, causing the curve to spike again. Slowly,
the minimum failure rate level begins to rise—the software is
deteriorating due to change.
3. Although the industry is moving toward component-based construction,
most
software continues to be custom built.
The reusable components have been created so that the engineer can
concentrate on the truly innovative elements of a design, that is, the
parts of the design that represent something new.
🔸In the software world, it is something that has only begun to be
achieved on a broad scale. A software component should be designed and
implemented so that it can be reused in many different programs.
🔸A software component should be designed and implemented so that it can
be reused in many different programs. Modern reusable components
encapsulate both data and the processing that is applied to the data,
enabling the software engineer to create new applications from reusable
parts.
🔸For example, today’s interactive user interfaces are built with
reusable components that enable the creation of graphics windows,
pull-down menus, and a wide variety of interaction mechanisms.
4. A software component should be designed and implemented so that it can
be
reused in many different programs.
🔸It is the responsibility of software engineer to design and implement
a software component in such a way that it should be reused easily
in many different programs.
🔸Latest reusable components summarize both data as well as
the processing, which is applied to the data, which helps the
software engineer to develop new applications from existing
components.
🔳Types / Categories of Software
1️⃣System Software
2️⃣Application Software
3️⃣Scientific Software
4️⃣Embedded Software
5️⃣Real time Software
6️⃣Product-line Software
7️⃣Web based software
8️⃣Artificial Intelligence (AI) Software
9️⃣Personal Computer Software
1. System Software
➡️System Software comprises programs that control the operations of the
hardware components. System software is a collection of programs used to run
the system as assistance to other software programs.
➡️The compilers, editor, utilities, operating system components, drivers,
and interfaces are examples of system software.
➡️System software resides in the computer system and consumes its
resources. A computer system software cannot function.
➡️System software directly interacts with the hardware, heavy usage by
multiple users, concurrent operations that require scheduling, resource
sharing, and so on.
2. Application Software
➡️Application software consists of programs purely for the tasks of the
users, obtaining the inputs and processing them in the instructions already
defined.
➡️Application software is a standalone program which solves a specific
business/ organization requirement.
➡️Application software consists of the programs that do real work for the
users. For example, word processors, spreadsheets and database management
systems fall under the category of applications software.
3. Embedded Software
➡️Software, when written to perform certain functions under control
conditions and is further embedded into hardware as a part of large systems,
is called embedded software.
➡️Found in intelligent products for consumer and industrial markets.
➡️Resides in read-only memory (ROM), used to control products and systems.
➡️Can perform very limited tasks or provide significant control (such as
automotive features).
➡️Examples: Microwave ovens, washing machines.
4. Personal Computer Software
➡️Developed for use on personal computers, both for business and personal
applications.
➡️Broad range includes word processing, spreadsheets, graphics, multimedia,
and database management.
➡️Facilitates external network/database access and entertainment.
➡️Examples: Microsoft Word, Excel.
5. Scientific Software
➡️Characterized by number-crunching and intensive algorithms.
➡️Used in scientific research such as astronomy, biology, and engineering
(stress analysis, CAD/CAM).
➡️Modern types use more interactive and real-time features.
➡️Examples: CAD and CAM software.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Software
➡️Simulates human intelligence and decision-making.
➡️Features learning, reasoning, problem-solving abilities.
➡️Used in applications like expert systems, natural language processing,
and robotics.
➡️Continuously improves performance with experience.
🔳Software Characteristics
1. Software is Developed or Engineered, Not Manufactured
🔸Software creation is an engineering process, not a manufacturing
one.
🔸High quality is achieved through good design, unlike hardware where
manufacturing can introduce defects.
🔸Software project costs are concentrated in engineering/design, not in
reproduction.
🔸Software projects should not be managed as if they were manufacturing
projects because of these fundamental differences.
2. Software Doesn't Wear Out
🔸Software does not physically degrade over time like hardware.
🔸However, as changes are made (maintenance), new defects are likely to be
introduced, causing the software to “deteriorate.”
🔸The failure rate curve of software does not show wear, but spikes with
each change due to newly introduced defects.
🔸Over its life, ongoing changes can raise the minimum failure rate,
reflecting deterioration due to change rather than physical wear.
3. Most Software is Still Custom-Built
🔸While the industry is moving towards component-based construction, most
software continues to be tailored for specific needs.
🔸Reusable components allow engineers to focus on innovative aspects of a
design.
🔸True large-scale reuse is only now becoming widespread.
🔸Custom-built nature means software is often unique and specifically
crafted for different users or organizations.
4. Software Can Be Reused
🔸Well-designed software components can be reused in different
programs.
🔸Modern reusable components encapsulate both data and the processing
applied to it.
🔸User interfaces, for example, are built with reusable graphical
components (windows, menus, etc.).
🔸Reusing components helps speed up development and enhances productivity
by leveraging existing solutions.
🔳Software Development Framework
A Software Development Framework provides a structured foundation for
successful software development by organizing and guiding key activities
throughout a project's life cycle.
Key Components of the Software Development Framework
1. Process Framework
➡️Establishes the foundation for a complete software process.
➡️Identifies a small number of framework activities applicable to all
software projects:
🔸Communication: Heavy collaboration
with customers and stakeholders; encompasses requirements gathering and
related activities.
🔸Planning: Establishes plans for
software engineering work, describes technical tasks, risk analysis,
project tracking, and deadlines.
🔸Modeling: Creation of models to help
developers and customers understand requirements and designs.
🔸Construction: Involves both code
generation and the testing required for identifying defects.
🔸Deployment: Delivering the software to the
customer for evaluation and feedback.
➡️Umbrella activities such as software quality assurance and
configuration management occur throughout the process.
2. The 4 Ps of the Management Spectrum
➡️People: Focus on motivating, organizing, and developing the software
team.
➡️Product: Establishing clear product objectives and scope before planning
begins.
➡️Process: The chosen software process provides the necessary framework for
planning and execution.
➡️Project: Careful planning and control to manage complexity and improve
success rates.
3. Framework Activities and Adaptation
➡️A small set of framework activities (listed above) is adapted by creating
specific task sets (tasks, milestones, work products, quality points) to
suit the project’s particular needs.
➡️Framework adapts to differences in project size, complexity, and team
requirements.
4. Prescriptive vs. Agile Models (Framework Styles)
➡️Prescriptive Model: Emphasizes detailed definitions and predictable
planning. Follows structured process life cycles like the Waterfall or
Spiral Model.
➡️Agile Model: Focuses on adaptability and people, using iterative,
incremental development and minimal documentation. Emphasizes continuous
feedback and adaptive planning.
🔳Software Process Framework
🔸A Software Process Framework is a structured approach that defines the
steps, tasks, and activities involved in software development.
🔸This framework serves as a foundation for software engineering, guiding
the development team through various stages to ensure a systematic and
efficient process.
🔸A Software Process Framework helps in project planning, risk
management, and quality assurance by detailing the chronological order of
actions.

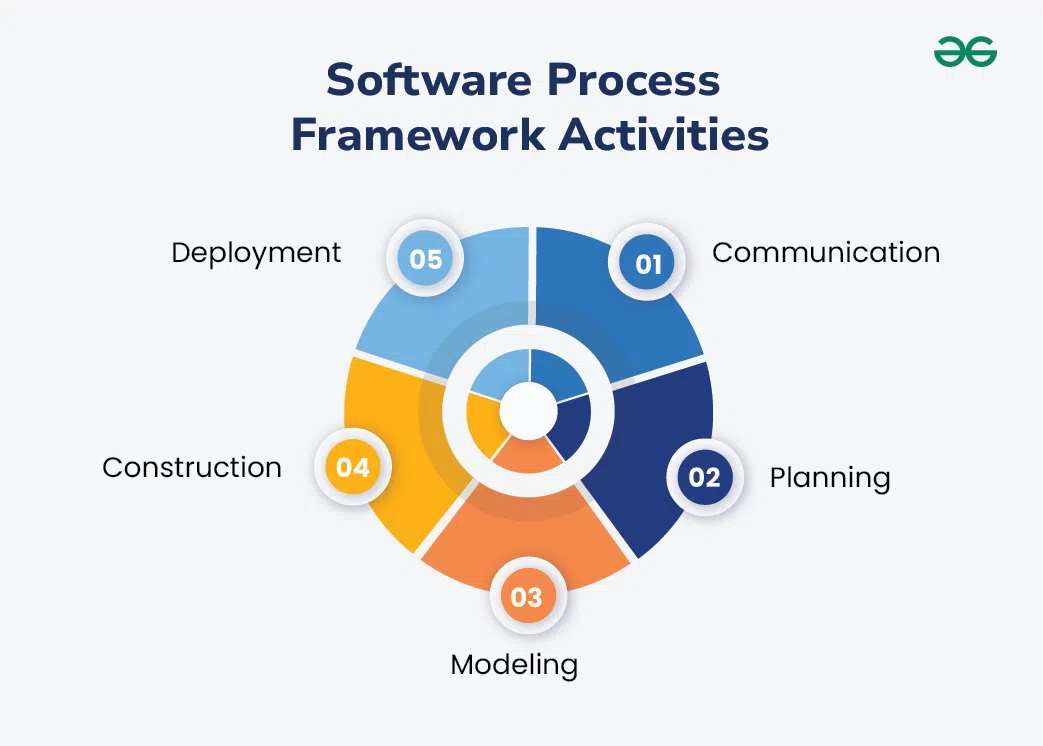
🔸Five framework activities are described in a process framework for
software engineering. Communication, planning, modeling, construction, and
deployment are all examples of framework activities.
1. Communication
Communication involves gathering requirements from customers and
stakeholders to determine the system's objectives and the software's
requirements.
Effective communication is essential to understand what the users need
from the software.
This phase ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page regarding
the goals and requirements of the system.
Activities: Requirement Gathering, Objective Setting.
2. Planning
Planning involves establishing an engineering work plan, describing
technical risks, listing resource requirements, and defining a work
schedule.
Planning helps in organizing the project and setting clear expectations.
It ensures that the development team has a roadmap to follow and that
potential challenges are anticipated and managed.
Activities: Work Plan, Risk Assessment, Resource
Allocation, Schedule Definition.
3. Modeling
Modeling involves creating architectural models and designs to better
understand the problem and work towards the best solution.
Modeling translates requirements into a visual and structured
representation of the system. It helps in identifying the best design
approach and serves as a blueprint for development.
Activities: Analysis of Requirements, Design.
4. Construction
Construction involves creating code, testing the system, fixing bugs,
and confirming that all criteria are met.
This phase is where the actual software is built. Testing is crucial to
ensure that the code is error-free and that the software meets all
specified requirements.
Activities: Code Generation, Testing.
5. Deployment
Deployment involves presenting the completed or partially completed
product to customers for evaluation and feedback, then making necessary
modifications based on their input.
Activities: Product Release, Feedback Collection, Product
Improvement.
🔳Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is a way to make software (or do any project) step by
step. You finish one step completely before you move to the next
step.
[ वॉटरफॉल मॉडेल म्हणजे सॉफ्टवेअर (किंवा कोणतेही प्रोजेक्ट)
टप्प्याटप्प्याने बनवायची पद्धत. एक टप्पा पूर्ण झाला की मगच पुढचा टप्पा
सुरु केला जातो. ]
Waterfall is best when you know exactly what you want at the
beginning!
[ वॉटरफॉल हा मॉडेल तेव्हा योग्य, जेव्हा सुरुवातीपासून सगळं स्पष्ट
माहित असतं! ]

1. Communication (Requirement Gathering)
Talk to your customer about what the software should do. List EVERY
requirement.
[ कम्युनिकेशन (आवश्यकता गोळा करणे) :- ग्राहकाशी संवाद साधून,
त्यांना काय हवं आहे हे नीटहीट समजून घेणे आणि लिहून ठेवणे. ]
2. Planning
Plan the schedule, estimate time and cost, and identify any risks.
[ वेळापत्रक, खर्च, धोके ओळखणे व सर्वांचे नियोजन करणे. ]
3. Modelling (Design)
The engineers/designers make plans for how the software will look and
work.
[ इंजिनिअर किंवा डिझायनरने सॉफ्टवेअर कसे दिसेल, कसे चालेल याचे
डिझाईन तयार करणे. ]
4. Construction (Coding)
Programmers write the code to create the software as per the
design.
[ प्रोग्रामर प्रत्यक्ष सॉफ्टवेअर कोड लिहितात. ]
5. Deployment (Delivery)
The software is given to the customer. They start using it, and if they
find bugs, they report back for fixes.
[ सॉफ्टवेअर ग्राहकाला दिलं जातं, वापरता येतं, त्रुटी असल्यास कळवता
येतं. ]
⭕Advantages: Easy To understand , Good for small project , easy to
manage.
❌Disadvantages: Not Good for large projects, takes time , No Changes
Allowed.
➡️ 1) Software is developed or engineered : Software is not manufactured
in the classical sense. Although some similarities exist between
software development and hardware manufacture, the two activities are
fundamentally different. Both activities are dependent on people, but
the relationship between people applied and work accomplished is entirely
different.
2) Software doesn't "wear out". During its life, software will
undergo change (maintenance). As changes are made, it is likely that some
new defects will be introduced, causing the failure rate curve to
spike. Before the curve can return to the original steady-state
failure rate, another change is requested, causing the curve to spike
again. Slowly, the minimum failure rate level begins to rise—the software
is deteriorating due to change.
3) Most Software is custom built, rather than being assembled from
Existing Components.
➡️ Embedded software, personal software, scientific software, Application
Software, system software.



.jpeg)



0 Comments
Hi, Viewers Do not Enter Spam Messages in comments