CLOUD COMPUTING
Assignment No. 1
1) What is Cloud Computing ?
Ans. Cloud computing is a model for delivering various computing services, such as servers, storage, software, and analytics, over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
2) Define cloud service.
Ans. Cloud services are IT resources, such as software and infrastructure, that are hosted by third-party providers and delivered over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
3) What is public cloud?
Ans. A public cloud is a cloud deployment model in which cloud resources are offered over the internet and open to all users and organizations.
4) What is private cloud?
Ans. A private cloud is a cloud computing model where a single organization has exclusive access to a dedicated cloud infrastructure, which can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
5) What is community cloud?
Ans. A community cloud is a cloud computing environment where the IT infrastructure and resources are shared by a specific group of organizations that have common interests or concerns, such as security, compliance, or mission.
6) What is hybrid cloud?
Ans. A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud services, giving businesses the best of both worlds—scalability from public clouds and security from private clouds.
7) Explain PaaS ?
Ans. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model designed for developers, offering a complete environment to build, test and deploy applications.
PaaS takes care of things like servers, storage and networking allowing developers to focus mainly on writing code and delivering applications quickly.
In the cloud computing ecosystem, PaaS acts as a middle layer between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Services Provided by PaaS:
1. Scalability
2. Application Design and Development
3. Testing and Deployment
4. Web Service Integration
5. Data Security
6. Database Integration
Advantages of PaaS:
1. Simple and easy
2. Cost Efficiency
3. Vendor Lock-in
4. Focus on Software Development
Disadvantages of PaaS:
1. Limited Customization
2. Performance Limits
3. Limited Control
4. Security Concerns
Uses of PaaS:
Application Development, Big Data and Analytics, etc.
Examples: AWS , Google App Engine, Heroku.
Overall, PaaS is a game-changer for modern software development and a key driver of digital transformation.
8) Explain IaaS?
Ans. IaaS is a cloud service model where the cloud provider delivers infrastructure components such as servers, storage, networking, and virtualization to customers.
The users manage operating systems, applications, and data, while the provider manages the underlying hardware and virtualization layer.
Key Components of IaaS:
1.Compute – Virtual machines (VMs) or instances to run applications.
2.Storage – Scalable storage options like block storage, object storage.
3.Networking – Virtual networks, load balancers, IP addresses.
4. Virtualization – Hypervisors to run multiple VMs on a single physical server.
Features:
On-demand scalability
Pay-as-you-go pricing
High availability and reliability
Self-service provisioning
Eliminates need for physical infrastructure
Examples of IaaS Providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
Google Compute Engine
IBM Cloud
Use Cases:
Hosting websites and applications
Backup and disaster recovery
Big data analytics
Development and testing environments
IaaS Providers: Google cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, AWS Cloud, etc.
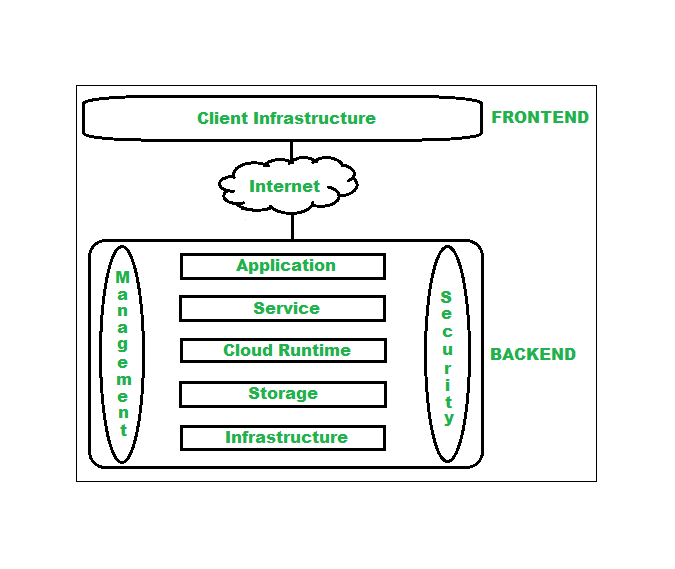
9) Explain cloud computing architecture with diagram ?
Ans. Cloud Computing, is one of the most demanding technologies of the current time and is giving a new shape to every organization by providing on-demand virtualized services/resources.
Architecture of cloud computing is the combination of both SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) and EDA (Event Driven Architecture).
Client infrastructure, application, service, runtime cloud, storage, infrastructure, management and security all these are the components of cloud computing architecture.
The cloud architecture is divided into 2 parts, i.e.
1. Frontend: Frontend of the cloud architecture refers to the client side of cloud computing system.
2. Backend: Backend refers to the cloud itself which is used by the service provider.
Components of Cloud Computing Architecture:
Client Infrastructure, Service, Storage, Runtime Cloud, Infrastructure, Management, etc.
Cloud Computing Architecture Example:
1. Online Learning App
2. Online Store
3. Mobile App Backend (Food Delivery App)
Benefits of Cloud Computing Architecture:
Makes overall cloud computing system simpler.
Improves data processing requirements.
Helps in providing high security.
Makes it more modularized.
Results in better disaster recovery.
Gives good user accessibility.
Reduces IT operating costs.
Provides high level reliability.
Scalability.
Components of Cloud Architecture:
1. Front-End (Client Side):
Includes the user interface, client devices, and applications to access cloud services (e.g., web browsers, mobile apps).
2. Back-End (Server Side):
Application: Software that provides services to clients.
Storage: Stores data securely.
Database: Manages data efficiently.
Virtualization: Enables resource sharing.
Servers: Provide computing power.
Security Management: Ensures data protection.
3. Cloud Service Models:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
SaaS (Software as a Service)
4. Cloud Deployment Models:
Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, Community Cloud.
5. Network:
Internet connects the client side to the cloud infrastructure.
10) Explain characteristics of cloud computing?
Ans.
1. Broad network access: The Computing services are generally provided over standard networks and heterogeneous devices.
2. Multi-tenancy: Cloud computing providers can support multiple tenants (users or organizations) on a single set of shared resources.
3. Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect their users' data and ensure the privacy of sensitive information.
4. Automation: Cloud computing services are often highly automated, allowing users to deploy and manage resources with minimal manual intervention.
5. Resilient computing: Cloud computing services are typically designed with redundancy and fault tolerance in mind, which ensures high availability and reliability.
6. Virtualization: Cloud computing providers use virtualization technology to abstract underlying hardware resources and present them as logical resources to users.
11) State how cloud is cost beneficial.
Ans. Cloud computing is cost beneficial because:
1. Pay-as-You-Go Model:
You pay only for the resources you use, reducing unnecessary expenses.
2. No Upfront Hardware Cost:
Eliminates the need to purchase expensive servers and infrastructure.
3. Reduced Maintenance Cost:
Cloud provider handles updates, security, and maintenance.
4. Scalability and Flexibility:
Scale resources up or down as per demand, avoiding over-provisioning costs.
5. Energy and Space Savings:
No need for on-site data centers, reducing electricity and space costs.
12) Write down applications of cloud?
Ans. Applications of Cloud Computing:
Data Storage & Backup – Store and retrieve data securely.
Web Hosting – Hosting websites and applications.
SaaS – Software services like Gmail, Google Docs.
Big Data Analytics – Analyze large datasets.
Disaster Recovery – Backup and restore solutions.
Assignment No. 2
1) What is virtualization?
Ans. Virtualization is a foundational technology in cloud computing enabling efficient use of physical hardware by creating multiple virtual environments on a single system.
2) What are the benefits of virtualization?
Ans. Benefits of Virtualization:
1. Better utilization of hardware resources.
2. Reduces cost of hardware and maintenance.
3. Provides isolation, security, and easier backup.
4. Supports scalability and disaster recovery.
5. Testing & Development
3) What are the characteristics of virtualization?
Ans. characteristics of virtualization:
1. Partitioning – A single physical server can run multiple virtual machines.
2. Isolation – Each VM is independent; one VM’s issues do not affect others.
3. Encapsulation – A VM is stored as files, making it portable and easy to back up.
4. Hardware Independence – VMs can run on different hardware as long as a hypervisor is available.
5. Portability – VMs can be migrated across servers with minimal effort.
6. Resource Pooling – CPU, memory, and storage are pooled and allocated to VMs dynamically.
7. Scalability – Resources can be scaled up or down quickly by creating or resizing VMs.
8. Centralized Management – Administrators can manage all VMs from one platform.
9. Efficiency – Maximizes hardware utilization by running multiple workloads.
10. Flexibility – Supports different operating systems and applications on the same physical server.
4) Explain block level virtualization and file level virtualization.
Ans.
Block-Level Virtualization
Definition: Block-level virtualization abstracts and manages storage at the block level (the smallest unit of data storage, usually 512 bytes or 4 KB).
How it works: Instead of applications directly accessing physical disks, they interact with a virtualized storage system that maps logical blocks to physical storage blocks.
Usage: Commonly used in Storage Area Networks (SANs).
Advantages:
1. High performance and flexibility.
2. Allows pooling of storage from multiple devices into one logical storage unit.
3. Easier management of storage space.
File-Level Virtualization:
Definition: File-level virtualization abstracts storage at the file level, allowing users and applications to access files without needing to know their physical location.
How it works: A virtualization layer sits between clients and storage, redirecting file requests to the correct physical storage location.
Usage: Commonly used in Network Attached Storage (NAS).
Advantages:
1. Simplifies data access by hiding physical file locations.
2. Allows easy migration of files between servers without changing user paths.
3. Reduces downtime during file movement or storage upgrades.
5) What is software virtualization with its types?
Ans. Software virtualization is the process of creating a virtual environment for running multiple operating systems or applications on the same physical machine.
It separates applications and operating systems from the underlying hardware, allowing better resource utilization, testing, and isolation.
Types of Software Virtualization:
1. Operating System Virtualization
2. Application Virtualization
3. Server Virtualization
4. Desktop Virtualization
5. Storage Virtualization
6. Network Virtualization
6) What are the benefits of storage virtualization?
Ans. Benefits of Storage Virtualization:
1. Better utilization of storage space.
2. Simplifies storage management.
3. Provides scalability for future growth.
4. Ensures high availability and reliability.
5. Improves system performance.
6. Enables easy data migration.
7. Reduces storage cost.
8. Supports backup and disaster recovery.
7) Describe disadvantages of virtualization.
Ans. While virtualization offers many benefits, it also has some drawbacks:
High Initial Cost – Setting up virtualization infrastructure (servers, storage, licensing) can be expensive.
Performance Overhead – Virtual machines may run slower than physical machines due to resource sharing.
Complex Management – Requires skilled administrators to configure and manage virtual environments.
Security Risks – If the hypervisor is attacked, all hosted VMs are at risk.
Resource Contention – Multiple VMs on one host may compete for CPU, memory, and I/O resources, leading to bottlenecks.
Downtime Impact – If the physical server (host) fails, all VMs on it are affected.
Software Licensing Issues – Licensing for virtual environments can be complex and costly.
Compatibility Issues – Not all applications or OS versions work smoothly in a virtualized environment.
8) What is network virtualization?
Ans. It is the process of combining hardware and software network resources into a single virtual network. It allows multiple virtual networks to run on the same physical infrastructure.
Types:
1. Internal Network Virtualization
2. External Network Virtualization
Benefits: Efficient resource utilization, scalability, security, and simplified management.
9) Describe virtualization reference model with diagram.
Ans. Three major Components falls under this category in a virtualized environment:
1. GUEST:
The guest represents the system component that interacts with the virtualization layer rather than with the host, as would normally happen. Guests usually consist of one or more virtual disk files, and a VM definition file. Virtual Machines are centrally managed by a host application that sees and manages each virtual machine as a different application.
2. HOST:
The host represents the original environment where the guest is supposed to be managed. Each guest runs on the host using shared resources donated to it by the host. The operating system, works as the host and manages the physical resource management, and the device support.
3. VIRTUALIZATION LAYER:
The virtualization layer is responsible for recreating the same or a different environment where the guest will operate. It is an additional abstraction layer between a network and storage hardware, computing, and the application running on it. Usually it helps to run a single operating system per machine which can be very inflexible compared to the usage of virtualization.
Assignment No. 5
1) Enlist any four cloud platforms
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS):
·
Provides a wide range of cloud services like
EC2, S3, and Lambda.
·
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud platform
offered by Amazon that lets people and companies use IT services like storage,
servers, and databases through the internet.
2. Microsoft Azure:
·
Offers virtual machines, AI tools, and cloud
databases.
·
Microsoft Azure is a public cloud platform that
offers Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and
Software as a Service (SaaS).
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
·
Supports big data, machine learning, and storage
services.
·
Google Cloud Platform is a public
cloud service that delivers infrastructure, platform, and
software services hosted on Google’s highly reliable and scalable
infrastructure.
4. IBM Cloud:
·
Provides hybrid cloud and AI-powered cloud
services.
·
IBM Cloud is a cloud computing platform and
infrastructure that offers computing, storage, networking, AI, blockchain,
DevOps, and more services to businesses.
2) Explain working of Amazon EC2 and S3 cloud platform
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Amazon EC2 is a part of Amazon Web
Services (AWS) that provides virtual servers (instances) in the cloud. It
allows users to run applications, host websites, or perform computations
without needing to buy and maintain physical hardware.
EC2 provides resizable virtual servers on demand, offering
flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency for deploying applications.
EC2 provides virtual machines to run applications.
The EC2 Workflow (How it Works)
Here are the steps in a concise workflow:
- Select
AMI : Choose an Amazon Machine Image (the server's software
template, including the OS).
- Choose
Instance Type : Select the hardware specifications (CPU, RAM, storage)
needed for your workload.
- Configure
Networking and Security : Define the Security Group (virtual
firewall rules) and select the VPC (virtual network) for the
instance.
- Create
Key Pair : Generate or select a key pair for secure remote
connection (e.g., SSH).
- Launch
Instance : Start the virtual machine based on your selections.
- Connect
and Use : Access the running instance securely and deploy your
application or perform your computing tasks.
- Scale
and Terminate : Use Auto Scaling to adjust capacity as demand
changes, and terminate the instance when finished to stop billing.
1. Provides scalable virtual servers.
2. Users choose instance type, OS, and configuration.
3. Automatically scales as per demand.
4. Pay-as-you-go billing model.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service):
Amazon S3 is an object storage service that allows users to store and retrieve
any amount of data at any time over the internet. It is highly durable,
scalable, and secure.
S3 provides scalable object storage to store and retrieve
data.
Amazon S3 is a secure, scalable object storage solution
ideal for backups, static website hosting, media storage, and data archiving.
How
S3 Works (Core Concepts)
S3 is built on a simple, flat
structure using two main concepts:
- Buckets:
A bucket is the fundamental container for data stored in S3.
- It's
a logical container for your files and is analogous to a top-level folder
on your hard drive.
- Objects:
The data unit stored in an S3 bucket.
- An object consists of the data file (of any
type: photo, video, document, etc.) plus any associated metadata.
1. Used for storing and retrieving any amount of data.
2. Data organized into buckets and objects.
3. Supports lifecycle policies and encryption.
4. Highly durable and scalable.
3) Enlist technologies in IoT
1. Sensors and Actuators: A sensor is a device that detects or measures
physical properties from the environment (like temperature, light, motion,
humidity, pressure, etc.) and converts them into electrical signals that can be
processed by a computer or cloud system. An actuator is a device that converts
electrical signals into physical actions or movements. It is used to control or
manipulate physical systems based on commands from a controller or cloud
platform.
2. Connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, 5G): In cloud computing and
Internet of Things (IoT) environments, connectivity is the backbone that allows
sensors, actuators, and devices to communicate with each other and send data to
the cloud for processing. Different wireless communication technologies are
used based on range, speed, power consumption, and cost.
3. Cloud and Edge Computing: Both Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
are important technologies for data processing, storage, and application
deployment. But they differ mainly in where the data is processed.
4. Big Data and Analytics: Big Data refers to extremely large and
complex datasets that are too big to be processed and managed by traditional
data-processing tools. Cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft
Azure provide scalable infrastructure and tools for storing and analyzing big
data without needing physical servers.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
6. IoT Platforms (AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub)
7. Security Protocols (TLS, OAuth)
8. Embedded Systems
4) Differentiate between OpenNebula and OpenStack
|
OpenNebula
|
OpenStack
|
|
1. Lightweight and simple cloud management platform
|
1. Feature-rich and complex cloud management platform
|
|
2. Focuses on private and hybrid clouds
|
2. Suitable for private, public, and hybrid clouds
|
|
3. Easier to deploy and configure
|
3. Requires more time and expertise to deploy
|
|
4. Smaller community and fewer modules
|
4. Large community, many modules and services
|
|
5. Uses KVM, VMware, and LXD for virtualization
|
5. Supports KVM, Xen, VMware, Hyper-V, and more
|
|
6. Less resource-intensive
|
6. More resource-intensive
|
|
7. Offers basic features for VM management and cloud
orchestration
|
7. Offers advanced features like identity, object storage,
networking, and telemetry
|
|
8. Ideal for small to medium-scale cloud setups
|
8. Ideal for large-scale enterprise clouds
|
|
9. GUI and CLI are simpler and more user-friendly
|
9. GUI (Horizon) and CLI are powerful but more complex
|
|
10. Focused on simplicity and quick deployment
|
10. Focused on scalability, modularity, and flexibility
|
5) Differentiate between Amazon EC2 and Google AppEngine
|
Amazon EC2
|
Google App
Engine
|
|
1. IaaS
(Infrastructure as a Service)
|
1. PaaS
(Platform as a Service)
|
|
2. Provides
virtual servers (instances)
|
2. Provides
platform to deploy applications
|
|
3. User
manages OS, runtime, and software
|
3. Google
manages OS and runtime
|
|
4. Manual or
user-configured scaling
|
4. Automatic
scaling built-in
|
|
5. Full
control over server environment
|
5. Limited
control, focus on code only
|
|
6. Suitable
for custom apps and databases
|
6. Suitable
for web and mobile apps
|
|
7. User
handles updates and maintenance
|
7. Google
handles updates and maintenance
|
|
8. Launch
time may take minutes
|
8. Faster
deployment, environment ready
|
|
9. Pay for
compute, storage, and network
|
9. Pay for
app usage (requests, storage)
|
|
10. Flexible
but requires technical knowledge
|
10. Easy for
developers, minimal setup
|
6) Describe working of Google AppEngine
1. Developer uploads the web app to AppEngine.
2. AppEngine allocates resources automatically.
3. It scales applications based on traffic.
4. Uses sandboxed environment for isolation.
5. Provides built-in services (Datastore, Memcache, Task Queue).
6. Handles load balancing and monitoring automatically.
7. Supports multiple programming languages.
8. Pay only for resources used.
GAE is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) that allows developers
to build and deploy web applications and APIs without managing servers.
It automatically handles infrastructure, scaling, and
maintenance, so developers can focus on writing code.
Working
- Develop
Application
- Write
code in supported languages (Python, Java, Node.js, Go, PHP, Ruby).
- Design
apps for web, mobile backends, or APIs.
- Upload
Code to GAE
- Use gcloud
CLI or Google Cloud Console to deploy code.
- Code
is uploaded to Google Cloud Platform automatically.
- Automatic
Environment Setup
- GAE
provisions runtime environments automatically.
- No
need to configure servers, OS, or web servers manually.
- Automatic
Scaling
- Monitors
incoming traffic to scale instances up or down.
- Ensures
app handles high or low demand efficiently.
- Request
Handling
- User
requests are routed to available instances.
- Instances
process requests and return responses quickly.
- Load
Balancing
- Built-in
load balancers distribute traffic evenly.
- Prevents
any single instance from becoming overloaded.
- Managed
Services Integration
- Easily
connect with databases, caching, and messaging services.
- Reduces
complexity and speeds up application development.
- Monitoring
and Billing
- Logs,
metrics, and error reporting are provided automatically.
- Pay
only for resources used: compute time, storage, and bandwidth.



.jpeg)



0 Comments
Hi, Viewers Do not Enter Spam Messages in comments